Linux

How to Build acpidump from Source and use it to Debug Complex CXL and PCI Issues
This article is a detailed guide on how to build the latest version of the acpidump tool from its source code.
Read More
Is Your Application Really Using Persistent Memory? Here’s How to Tell.
Persistent memory (PMEM), especially when accessed via technologies like CXL, promises the best of both worlds: DRAM-like speed with the durability of an SSD.
Read More
How to Confirm Virtual to Physical Memory Mappings for PMem and FSDAX Files
Are you curious whether your application’s memory-mapped files are really using Intel Optane Persistent Memory (PMem), Compute Express Link (CXL) Non-Volatile Memory Modules (NV-CMM), or another DAX-enabled persistent memory device?
Read More
CXL Memory NUMA Node Mapping with Sub-NUMA Clustering (SNC) on Linux
CXL (Compute Express Link) memory devices are revolutionizing server architectures, but they also introduce new NUMA complexity, especially when advanced memory configurations, such as Sub-NUMA Clustering (SNC), are enabled.
Read More
Your Personal Codespace: Self-Host VS Code on Any Server
GitHub Codespaces and other cloud IDEs have revolutionized development, offering a complete VS Code environment that runs on a remote server and is accessible from any browser.
Read More
Unlock Your CXL Memory: How to Switch from NUMA (System-RAM) to Direct Access (DAX) Mode
As a Linux System Administrator working with Compute Express Link (CXL) memory devices, you should be aware that as of Linux Kernel 6.
Read More
Fastfetch: The Speedy Successor Neofetch Replacement Your Ubuntu Terminal Needs
If you love customizing your Linux terminal and getting a quick, visually appealing overview of your system specs, you might have used neofetch in the past.
Read More
Building NDCTL Utilities from Source: A Comprehensive Guide
Building NDCTL with Meson on Ubuntu 24.04 The NDCTL package includes the cxl, daxctl, and ndctl utilities.
Read More
Understanding STREAM: Benchmarking Memory Bandwidth for DRAM and CXL
In today’s Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and high-performance computing (HPC) landscape, memory bandwidth is a critical factor in determining overall system performance.
Read More
A Step-by-Step Guide on Using Cloud Images with QEMU 9 on Ubuntu 24.04
Introduction Cloud images are pre-configured, optimized templates of operating systems designed specifically for cloud and virtualized environments.
Read More
Understanding Memory Usage with `smem`
Memory management is crucial for Linux administrators and developers, especially when optimizing performance for resource-intensive applications.
Read More
A Practical Guide to Identify Compute Express Link (CXL) Devices in Your Server
In this article, we will provide four methods for identifying CXL devices in your server and how to determine which CPU socket and NUMA node each CXL device is connected.
Read More
How To Map a CXL Endpoint to a CPU Socket in Linux
When working with CXL Type 3 Memory Expander endpoints, it’s nice to know which CPU Socket owns the root complex for the endpoint.
Read More
Using Linux Kernel Memory Tiering
In this post, I’ll discuss what memory tiering is, why we need it, and how to use the memory tiering feature available in the mainline v5.
Read More
How To map VMWare vSphere/ESXi PMem devices from the Host to Guest VM
In this post, we’ll use VMWare ESXi 7.0u3 to create a Guest VM running Ubuntu 21.
Read More
How To Emulate CXL Devices using KVM and QEMU
What is CXL? Compute Express Link (CXL) is an open standard for high-speed central processing unit-to-device and CPU-to-memory connections, designed for high-performance data center computers.
Read More
How To Build a custom Linux Kernel to test Data Access Monitor (DAMON)
DAMON is a data access monitoring framework subsystem for the Linux kernel.
Read More
Resolving commands 'Killed' on GCP f1-micro Compute Engine instances
When I want to perform a quick task, I generally spin up a Google GCP Compute Engine instance as they’re cheap.
Read More
How To Enable Debug Logging in ipmctl
The ipmctl utility is used for configuring and managing Intel Optane Persistent Memory modules (DCPMM/PMem).
Read More
How To Monitor Persistent Memory Performance on Linux using PCM, Prometheus, and Grafana
In a previous article, I showed How To Install Prometheus and Grafana on Fedora Server .
Read MoreUsing ltrace to see what ipmctl and ndctl are doing
Occasionally, it is necessary to debug commands that are slow. Or you may simply be interested in learning how the tools work.
Read More
How to Boot Linux from Intel® Optane™ Persistent Memory
Introduction In this article, I will demonstrate how to configure a system with Intel Optane Persistent Memory (PMem) and use part of the PMem as a boot device.
Read More
How to Boot Linux from Intel® Optane™ Persistent Memory
Introduction In this article, I will demonstrate how to configure a system with Intel Optane Persistent Memory (PMem) and use part of the PMem as a boot device.
Read More
How to build an upstream Fedora Kernel from source
I typically keep my Fedora system current, updating it once every week or two.
Read More
Linux Device Mapper WriteCache (dm-writecache) performance improvements in Linux Kernel 5.8
The Linux ‘dm-writecache’ target allows for writeback caching of newly written data to an SSD or NVMe using persistent memory will achieve much better performance in Linux Kernel 5.
Read More
"ipmctl show -memoryresources" returns "Error: GetMemoryResourcesInfo Failed"
Issue: Running ipmctl show -memoryresources returns an error similar to the following:
Read MoreIntel Optane Persistent Memory Modules report "Non-functional" state in ipmctl
Issue Executing ipmctl show-dimm to get device information shows the persistent memory modules in a ‘Non-functional’ health state, eg:
Read More
How To Set Linux CPU Scaling Governor to Max Performance
The majority of modern processors are capable of operating in a number of different clock frequency and voltage configurations, often referred to as Operating Performance Points or P-states (in ACPI terminology).
Read More
How To Verify Linux Kernel Support for Persistent Memory
Linux Kernel support for persistent memory was first delivered in version 4.
Read More
How To Extend Volatile System Memory (RAM) using Persistent Memory on Linux
Intel(R) Optane(TM) Persistent Memory delivers a unique combination of affordable large capacity and support for data persistence.
Read More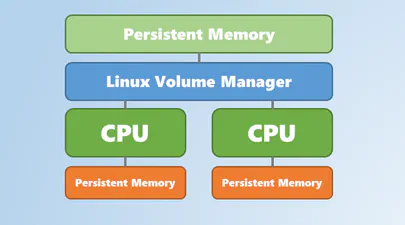
Using Linux Volume Manager (LVM) with Persistent Memory
In this article, we show how to use the Linux Volume Manager (LVM) to create concatenated, striped, and mirrored logical volumes using persistent memory modules as the backing storage device.
Read More